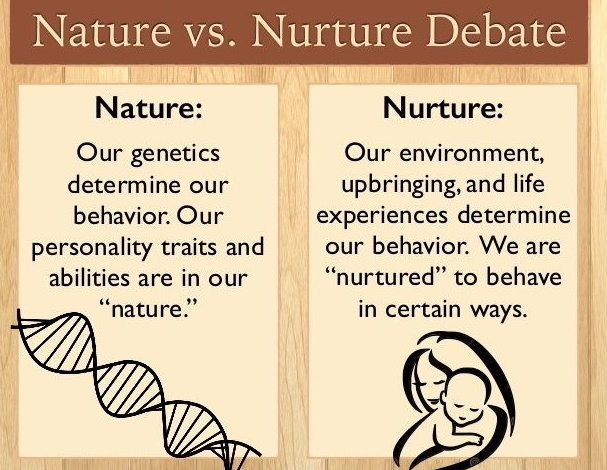
Twin studies- nature vs. nurture involve the study effects of genetics and environment on a given trait. These studies differentiate between the effects of genes acquired at birth and those exerted by different environments during their lives. This study shows the difference between nature and nurture.
Twin studies allow us to estimate how much of a trait comes from our genes and how much is influenced by the environment.
Types of Twins
Identical Twins
They are products of one sperm and one egg that are divided into two embryos in an early stage of the pregnancy. These are also known as monozygotic twins because they are formed through the division of a single zygote. They are therefore genetically identical. They share 100% of their genes.
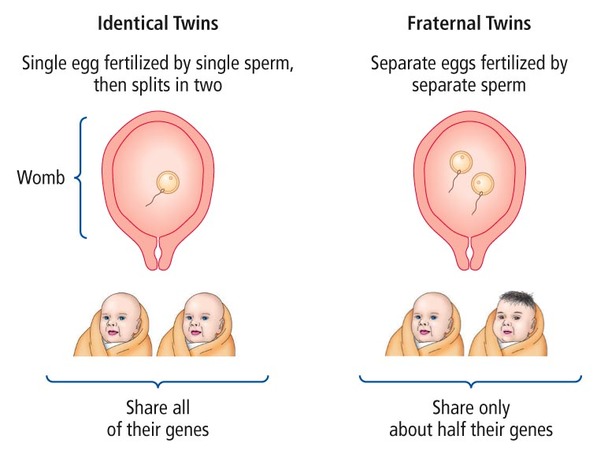
Non-identical or Fraternal Twins
They are derived from two different sperms and two different eggs. They are genetically similar to ordinary brothers and sisters but are born together and share, on average, 50% of their genes. These are also known as dizygotic twins because here two zygotes are formed.
Identical and fraternal twins all share the same environment as they grow up in the same family.
How do Twin studies work?
In twin studies, comparing similarities between identical twins with similarities between non-identical twins, it is possible to separate different influences.
Data are collected from multiple pairs of twins to get an accurate estimate of the relative importance of genes and environment.
Identical twins have similar genes as well as a similar environment. Differences between identical twins are possible only because of the non-shared influences of the environment. When identical twins are separated in infancy and raised apart are less similar than twins who are raised together.
If both identical and non-identical twins resemble closely to each other that is because of the shared environment. If identical twins resemble each other more closely than non-identical twins then it suggests that genetic factors play an important role here.
Importance of Twin studies
Twin studies provide information about the importance of genes and environment and thus provide information on where the balance lies between nature and nurture lies.
Twin studies play an important role in health and psychological research. The findings of the twin study help identify and treat various diseases and psychiatric disorders.
Twin studies show how psychological or medical disorders, behaviours and traits are influenced by genes and the environment. It helps us to prevent and treat various genetic disorders.
The investigation of variability became possible through genetics studies. Twin studies help in the study of the genetics of human behaviour. It verifies the genetic background of any disease.
Limitations of Twin studies
- Although twin studies are helpful, there are still some limitations. The assumption is that identical twins share 100% of their genes but this is not always true because of the process of mutation. The mutation leads to some small differences in identical twins. Here the twin studies do not give accurate results.
- Twin study results apply to the entire population in general and not just the individual. The expected results depend entirely on the statistical analysis. It fails to separate the effects of genes and the prenatal environment.
- Today genetics changed a lot and twin studies are still based on the earlier assumptions. We need a new method in twin studies for accurate results.
- There is research biasness.
Conclusion
Twin studies continue to inform about the relationship between genes and environment on a particular trait. There is some limitation revolving around the methods of twin studies but still, it is an important tool along with emerging genome and molecular research methods to throw light on the combined effects of human genetics and environment.
References
Twin Studies: A Unique Epidemiological Tool